What is the R-number in Covid?
In case of a pandemic, the R-number refers to the 'effective reproduction number' of the virus, and simply put, it's a way of measuring an infectious disease's ability to spread.
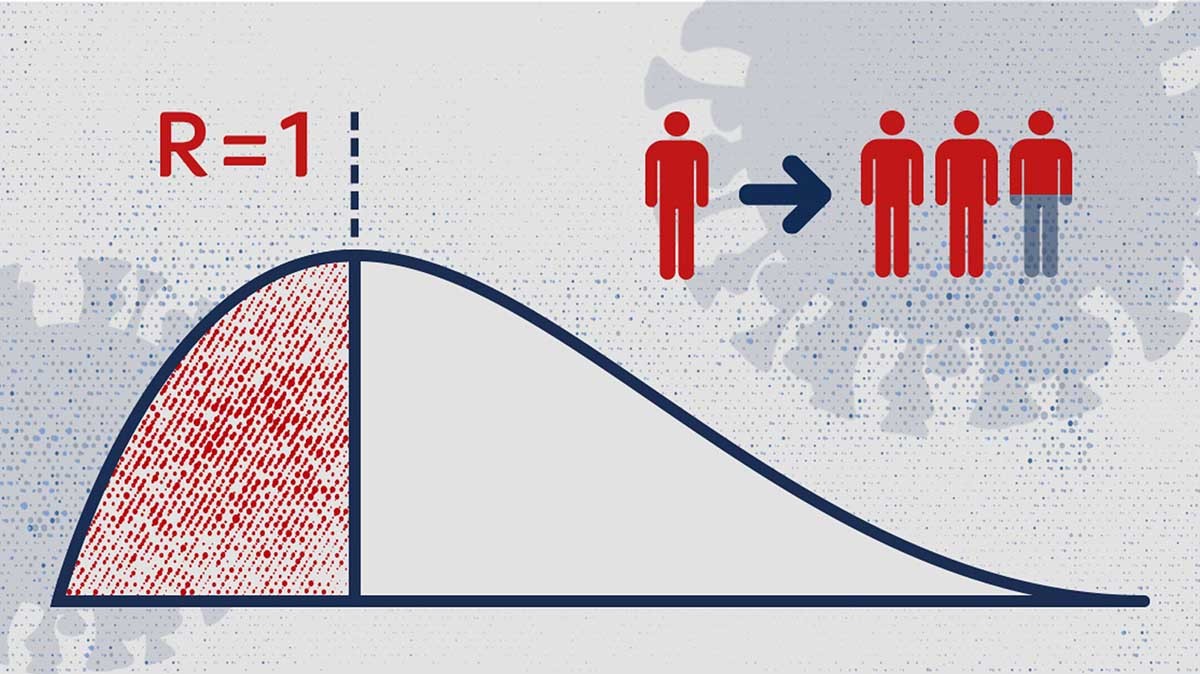
So for Covid [4] the R number quantify the average number of people that one infected person will pass the virus to. [1]
An R value of 1 is a crucial threshold, because the multiplier effect reduces, or in other words the infection tend to reduce its spread when R is lower than 1.
The R number isn't fixed, but can be affected by a range of factors, including not just how infectious a disease is but how it develops over time, how a population behaves, and any immunity already possessed thanks to infection or vaccination. Location is also important: a densely populated city is likely to have a higher R than a sparsely peopled rural area.
The R number is one of the big three.
Another is severity - some people have a very mild disease that does not cause many problems. But coronavirus and the disease it causes, Covid-19, can be severe and deadly.
The last is the number of cases, which is important for deciding when to act. If you have a high number, but ease restrictions so the reproduction number is about one, then you will continue to have a high number of cases.
A vaccination program, like the one currently under way in the UK, is another way to bring down the reproduction number.
A coronavirus patient would naturally infect three others on average, but if a vaccine could protect two of them from infection, then the reproduction number would fall from three to one.
Antibodies are proteins that bind to the body's foreign invaders (Covid virus) and signal the immune system to get to work. Simply put, they protect us from the viral infection.
But it is possible to have COVID-19 with no symptoms. [2]
That's because we may have the antibodies that block the virus to enter our cells , but that doesn't mean that the virus is not with us. So the virus may circulate in our body. We don't get sick, but we can still transmit the virus to others , which in turn may get sick because they do not have those antibodies.
An antibody test can tell you if it's likely you've had COVID-19 before. [3]
But it does not work for everyone, as some people who've had the virus do not have antibodies. It's still unclear if having antibodies stops you getting the virus again, and how long the antibodies may last.
An antibody test does not tell you:
[1] https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/05/covid-19-what-is-the-r-number/
[2] https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/how-to-stop-the-spread-of-coronavirus-covid-19/how-to-stop-the-spread-of-coronavirus-covid-19
[3] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronavirus-covid-19/testing/antibody-testing-to-check-if-youve-had-coronavirus/
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kcPLfVlHd3Y
So for Covid [4] the R number quantify the average number of people that one infected person will pass the virus to. [1]
An R value of 1 is a crucial threshold, because the multiplier effect reduces, or in other words the infection tend to reduce its spread when R is lower than 1.
The R number isn't fixed, but can be affected by a range of factors, including not just how infectious a disease is but how it develops over time, how a population behaves, and any immunity already possessed thanks to infection or vaccination. Location is also important: a densely populated city is likely to have a higher R than a sparsely peopled rural area.
The R number is one of the big three.
Another is severity - some people have a very mild disease that does not cause many problems. But coronavirus and the disease it causes, Covid-19, can be severe and deadly.
The last is the number of cases, which is important for deciding when to act. If you have a high number, but ease restrictions so the reproduction number is about one, then you will continue to have a high number of cases.
A vaccination program, like the one currently under way in the UK, is another way to bring down the reproduction number.
A coronavirus patient would naturally infect three others on average, but if a vaccine could protect two of them from infection, then the reproduction number would fall from three to one.
Antibodies are proteins that bind to the body's foreign invaders (Covid virus) and signal the immune system to get to work. Simply put, they protect us from the viral infection.
But it is possible to have COVID-19 with no symptoms. [2]
That's because we may have the antibodies that block the virus to enter our cells , but that doesn't mean that the virus is not with us. So the virus may circulate in our body. We don't get sick, but we can still transmit the virus to others , which in turn may get sick because they do not have those antibodies.
An antibody test can tell you if it's likely you've had COVID-19 before. [3]
But it does not work for everyone, as some people who've had the virus do not have antibodies. It's still unclear if having antibodies stops you getting the virus again, and how long the antibodies may last.
An antibody test does not tell you:
- if you're immune to COVID-19
- if you can or cannot spread the virus to other people
[1] https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/05/covid-19-what-is-the-r-number/
[2] https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/how-to-stop-the-spread-of-coronavirus-covid-19/how-to-stop-the-spread-of-coronavirus-covid-19
[3] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronavirus-covid-19/testing/antibody-testing-to-check-if-youve-had-coronavirus/
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kcPLfVlHd3Y